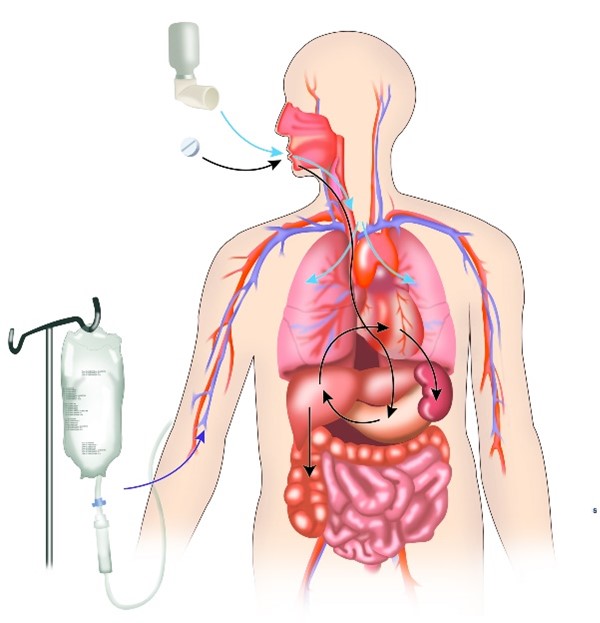
Have you ever wondered what happens inside your body when you take a medicine? An area of pharmacology called pharmacokinetics is the study of precisely that. Here, we follow a medicine as it enters the body, finds its therapeutic target (also called the active site), and then eventually leaves the body.
To begin, a person takes or is given a dose of medicine by a particular route of administration, such as by mouth (oral); through the skin (topical), mucous membranes
(nasal), or lungs (inhaled); or through a needle into a muscle (intramuscular) or into a vein (intravenous). Sometimes medicines can be administered right where they’re needed, like a topical antibiotic ointment on a scrape, but most medicines need to enter the blood to reach their therapeutic target and be effective. Those are the ones we’ll continue following, using the common pharmacokinetic acronym ADME: