Note to our Biomedical Beat readers: Echoing the sentiments NIH Director Francis Collins made on his blog, NIGMS is making every effort during the COVID-19 pandemic to keep supporting the best and most powerful science. In that spirit, we’ll continue to bring you stories across a wide range of NIGMS topics. We hope these posts offer a respite from the coronavirus news when needed.
Mitosis is fundamental among all organisms for reproduction, growth, and cell replacement. When a cell divides, it’s vital that the two new daughter cells maintain the same genes as the parent.
In one step of mitosis, chromosomes are segregated into two groups, which will go into the two new daughter cells. But if the chromosomes don’t divide properly, one daughter cell may have too many and the other too few. Having the wrong number of chromosomes, a condition called aneuploidy, can trigger cells to grow out of control.
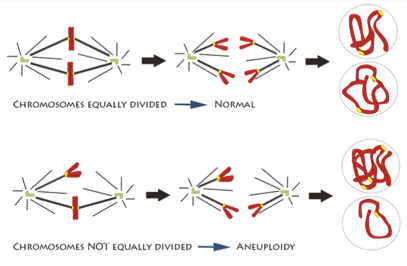
An illustration of chromosomes being segregated equally and unequally during mitosis. Credit: Deluca Lab, Colorado State University.
How chromosome segregation errors disrupt cell division is an important area of research. Although it’s been studied for decades, new aspects are still being uncovered and much remains unknown. NIGMS-funded scientists are studying different aspects of mitosis and chromosome segregation. Understanding the details can provide vital insight into an essential biological process and may also be the key to developing better drugs for cancer and other diseases.
Continue reading “How Errors in Divvying Up Chromosomes Lead to Defects in Cells”






 An illustration of chromosomes being segregated equally and unequally during mitosis. Credit: Deluca Lab, Colorado State University.
An illustration of chromosomes being segregated equally and unequally during mitosis. Credit: Deluca Lab, Colorado State University.