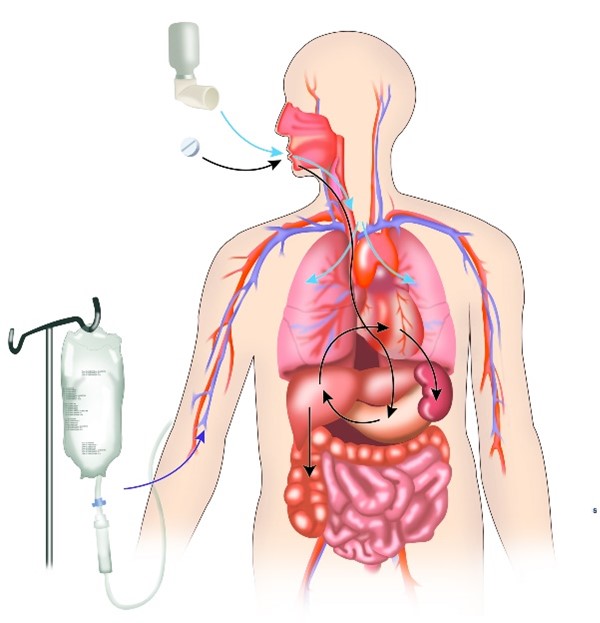
Pharmacologists research how the body acts on medicines (e.g., absorption, excretion) and how medicines act in the body, as well as how these effects vary from person to person. NIGMS-funded pharmacology researchers are:
- Conducting research to design medicines with fewer side effects
- Exploring how genes cause people to respond differently to medicines
- Developing new methods and molecular targets for drug discovery
- Discovering medicines based on natural products
- Understanding how medicines act using computers
- Monitoring brain function under anesthesia to develop safer anesthetic medicines that reduce side effects
- Creating artificial tissue to heal muscles after traumatic injuries
- Investigating how to treat patients with sepsis
- Measuring tissue damage from burns to help improve treatment options