This time of year, many creepy crawlies take center stage to frighten people of all ages. To celebrate Halloween, we’ve conjured up a slideshow of fascinating but spooky species that NIGMS-funded scientists study. Some of these creatures drink blood like vampires, while others—frogs, worms, flies, and salamanders—are perfect cauldron ingredients for a witch’s brew. Check out the slideshow—if you dare!
Continue reading “Slideshow: Creepy Crawlies”Category: Genes
Quiz: Gauge Your Genetics Knowledge

In our miniseries on genetics, we’ve introduced the genome and how variants in DNA affect us. We’ve also discussed how people inherit genetic information and the way genes are expressed, as well as common tools researchers use to study DNA. We hope you’ve paid close attention because it’s time to test your knowledge of genetics! Take our quiz below, and let us know how many questions you answered correctly.
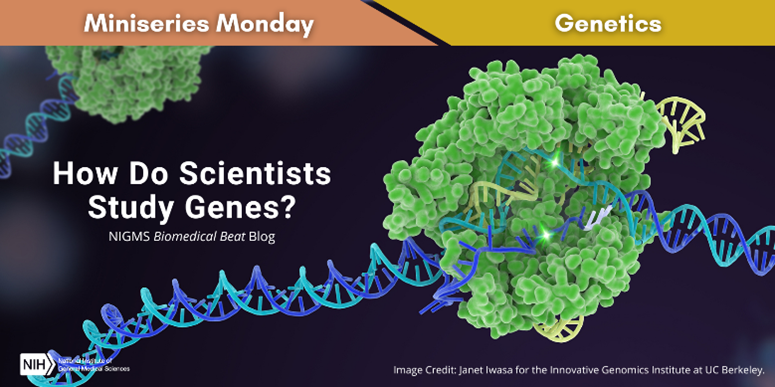
Continue reading “Quiz: Gauge Your Genetics Knowledge”How Do Scientists Study Genes?
You may wonder how scientists study something as tiny as DNA. Over the past decades, researchers have developed a wide range of tools and techniques to help them unlock the secrets of human genomes and those of other organisms. Two key examples are DNA sequencing and gene editing.
DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing, sometimes called gene or genome sequencing, enables researchers to “read” the order of the bases in a segment of DNA, which contains the information a cell needs to make important molecules like proteins, the functional building blocks of the cell. There are several methods for sequencing, but they all require many copies of the same DNA segment to get accurate results. Fortunately, scientists have developed a technique called polymerase chain reaction, often referred to as PCR, that can quickly and inexpensively create a large number of copies of a DNA segment.
Continue reading “How Do Scientists Study Genes?”How Are Physical Features and Health Conditions Inherited?
Have you ever been told that you have your mother’s eyes? Or maybe you’ve found that you and your father share a condition such as asthma? People who are biologically related often have similarities in appearance and health because they have some of the same genetic variants. However, you’ve likely noticed that siblings with the same biological parents can differ significantly. Each person’s genome is a combination of DNA from both of their parents, but siblings’ DNA can differ because of the mixing and matching involved in creating reproductive cells.
Continue reading “How Are Physical Features and Health Conditions Inherited?”Genetics by the Numbers
Even though scientists have been studying genetics since the mid-19th century, they continue to make new discoveries about genes and how they impact our health on a regular basis. NIGMS researchers study how genes are expressed and regulated, how gene variants with different “spellings” of their genetic code affect health, and much more. Get the drop on DNA and the gist of genes with these fast facts:
Continue reading “Genetics by the Numbers”What Is Genetics?
Genetics is the study of genes and heredity—how traits are passed from parents to children through DNA. A gene is a segment of DNA that contains instructions for building one or more molecules that help the body work. Researchers estimate that humans have about 20,000 genes, which account for about 1 percent of our DNA. The remainder of the DNA plays a role in regulating genes, and scientists are researching other potential functions.
Continue reading “What Is Genetics?”Propelling Rare Disease Research for More Than 50 Years

The year 2022 marked 50 years since the creation of the NIGMS Human Genetic Cell Repository (HGCR) at the Coriell Institute for Medical Research in Camden, New Jersey. The NIGMS HGCR consists of cell lines and DNA samples with a focus on those from people with rare, heritable diseases. “Many rare diseases now have treatments because of the samples in the NIGMS HGCR,” says Nahid Turan, Ph.D., Coriell’s chief biobanking officer and co-principal investigator of the NIGMS HGCR. She gives the example of a rare disease advocacy group who worked with the NIGMS HGCR to establish a cell line several decades ago. It was used to identify a gene associated with the disease, which aided in the development of five treatments that have received approval from the Food and Drug Administration.
Researchers have also studied NIGMS HGCR’s samples to help advance knowledge of basic biology and genetics, and even to support the development of a vaccine for a deadly virus.
Continue reading “Propelling Rare Disease Research for More Than 50 Years”Advancing American Indian and Alaska Native Health Through Research, Training, and Engagement
American Indian and Alaska Native (AI/AN) populations have long experienced health disparities such as higher rates of diabetes, certain cancers, and mental health conditions than those of other Americans. One contributing factor in these disparities is underrepresentation of AI/AN populations in biomedical science—as study participants, researchers, and health professionals. Unfamiliarity with health care options and opportunities, coupled with a distrust of biomedical research resulting from unethical studies in the past, have exacerbated this underrepresentation.
NIGMS-supported researchers, including Native scientists, are partnering with AI/AN Tribes to help reduce health disparities by conducting research focused on AI/AN health priorities and building infrastructure that supports research in those communities. They’re also preparing Native students to pursue careers in science and medicine. In this post, you’ll meet four scientists advancing AI/AN health.
Continue reading “Advancing American Indian and Alaska Native Health Through Research, Training, and Engagement”Career Conversations: Q&A with Biochemist Alexis Komor

“DNA is an amazingly beautiful molecule, and it’s so important. Each of our cells has only one copy of DNA, and if it gets damaged, that messes up everything else in the cell,” says Alexis Komor, Ph.D., an assistant professor of chemistry and biochemistry at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). Check out the highlights of our interview with Dr. Komor to learn about her scientific journey, research on DNA, and advice for students.
Q: How did you decide to study chemistry?
A: I really enjoyed math and science in middle and high school. When I applied to college, I knew I wanted to major in science over math because I felt like it was more relevant to what we experience on a day-to-day basis. I ultimately went into chemistry for a silly reason, but looking back now, I’m so very grateful that I did. Chemistry has this nice balance because it allows you to not only understand how things work on a molecular level but also see how those molecular workings relate to everyday phenomena—for example, understanding how DNA damage on a molecular level can lead to negative health outcomes.
Continue reading “Career Conversations: Q&A with Biochemist Alexis Komor”Hunting Disease-Causing Genetic Variants

“In my lab, we’ve been gene hunters—starting with visible phenotypes, or characteristics, and searching for the responsible genes,” says Miriam Meisler, Ph.D., the Myron Levine Distinguished University Professor at the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor. During her career, Dr. Meisler has identified the functions of multiple genes and has shown how genetic variants, or mutations, can impact human health.
Becoming a Scientist
Dr. Meisler had a strong interest in science as a child, which she credits to “growing up at the time of Sputnik” and receiving encouragement from her father and excellent science teachers in high school and college. However, when she started her undergraduate studies at Antioch College in Yellow Spring, Ohio, she decided to explore the humanities and social sciences. After 2 years of sociology and anthropology classes, she returned to biomedical science and, at a student swap, symbolically traded her dictionary for a slide rule—a mechanical device used to do calculations that was eventually replaced by the electric calculator.
Continue reading “Hunting Disease-Causing Genetic Variants”