Genes are segments of DNA. They contain instructions for building one or more molecules that help the body work. Researchers in the field of genetics study genes and heredity—how certain traits are passed from parents to their offspring through DNA. NIGMS supports many scientists who investigate the genetics of people and research organisms to better understand human health and disease.
Take our quiz below to test how much you know about genetics. For more quizzes and other fun learning tools, visit our activities and multimedia webpage.
Results
Share...
Share...

#1. Which of these is a part of DNA?
The correct answer is D. DNA molecules are shaped like twisted ladders where the rungs are pairs of four building blocks, or bases: guanine, cytosine, thymine, and adenine. Sequences of these bases contain instructions for building molecules, most of which are proteins.
Share...
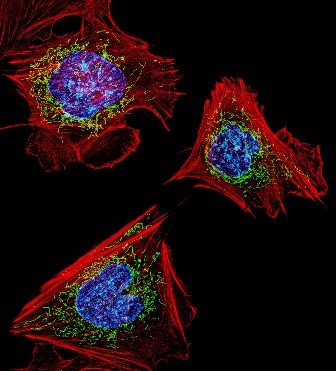
#2. Where do human, animal, and plant cells store genetic information (DNA)?
The correct answer is A. Genetic information is stored in a cellular compartment called the nucleus. To fit in this compartment, DNA must be tightly packed into structures known as chromosomes.
Share...
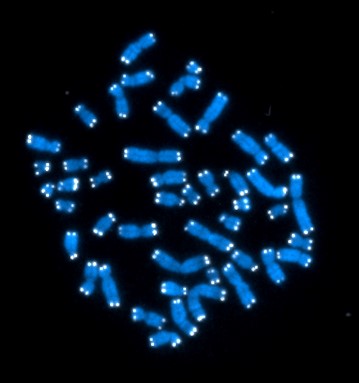
#3. How many genes do humans have, approximately?
The correct answer is C. Scientists estimate that humans have about 20,000 genes. A person’s genetic material is typically divided into 23 pairs of chromosomes in the nucleus.
Share...
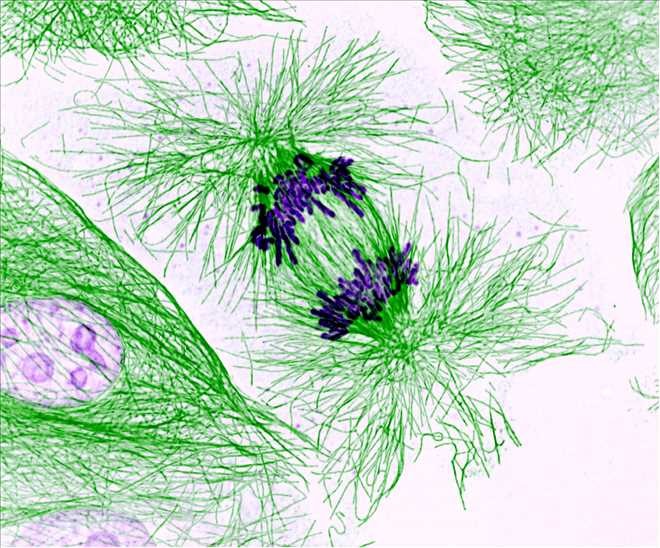
#4. What’s a genome?
The correct answer is B. A genome is all of an organism’s genetic material, including genes and other elements that control the genes’ activity. An organism’s entire genome is found in nearly every one of its cells.
Share...

#5. Which of these is a use for DNA sequencing?
The correct answer is D. DNA sequencing can shed light on a person’s health and ancestry, and it can help doctors make diagnoses. However, it can’t treat diseases.
Share...

#6. Which of these is NOT a reason geneticists study research organisms?
The correct answer is D. Humans and other organisms share many genes because all living things evolved from a common ancestor. Learn more about research organisms by reading our fact sheet.
Credit: iStock.





Hi,
I studied a little bit of genetics in 1968-70. The subject was new then, thanks to Dr. Hargovind Khurana, Now, at 74 & akone, I do not have time. Otherwise, I am interested even now. New developments!
Two questions are difficult to answer as they have not straightforward answers
Wow very interesting but some answers need more clarification