“There’s knowledge to seize in Puerto Rico, and our program is letting students know that they have a really important role to play in solving local problems, that they are part of the solution,” says Isar P. Godreau, Ph.D., a researcher at the University of Puerto Rico (UPR) Cayey Institute of Interdisciplinary Research.
Dr. Godreau, along with fellow researchers Mariluz Franco-Ortiz, Ph.D., at UPR Cayey Institute of Interdisciplinary Research, and Raymond Louis Tremblay, Ph.D., at UPR Humacao, directs an NIGMS Innovative Programs to Enhance Research Training (IPERT) grant. The UPR IPERT supports undergraduates throughout the university’s 11 campuses.
Resources Reach Thousands
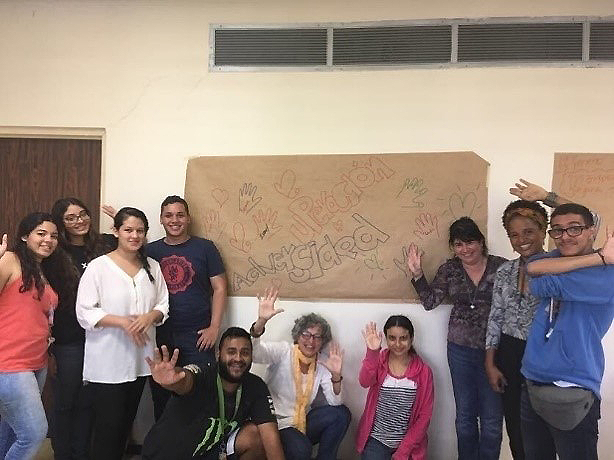

Dr. Franco-Ortiz (second from right) with students during a Coaching for Resiliency workshop session. Credit: Ivonne Bayron-Huertas, Ph.D.
Furthering NIGMS’ goals to create a highly skilled and diverse biomedical workforce, UPR IPERT provides undergraduate students from economically disadvantaged families with skills development and mentoring opportunities. One of the program’s main components is a series of Coaching for Resiliency workshops, which cover topics such as dealing with stress, managing family expectations, and handling financial challenges. A coach leads each group that includes about 10 to 15 first-year students and half as many second-year or higher students who act as peer mentors.
The coaching sessions help students connect with one another and with mentors. “One of the main accomplishments beyond the numbers is the power of networking,” says Dr. Franco-Ortiz. “The power of networking at different levels—from student mentors and faculty mentors at the UPR campus as well as abroad—is so crucial in terms of helping students who are looking for next steps.”
Continue reading “Preparing Students in Puerto Rico for Biomedical Careers”
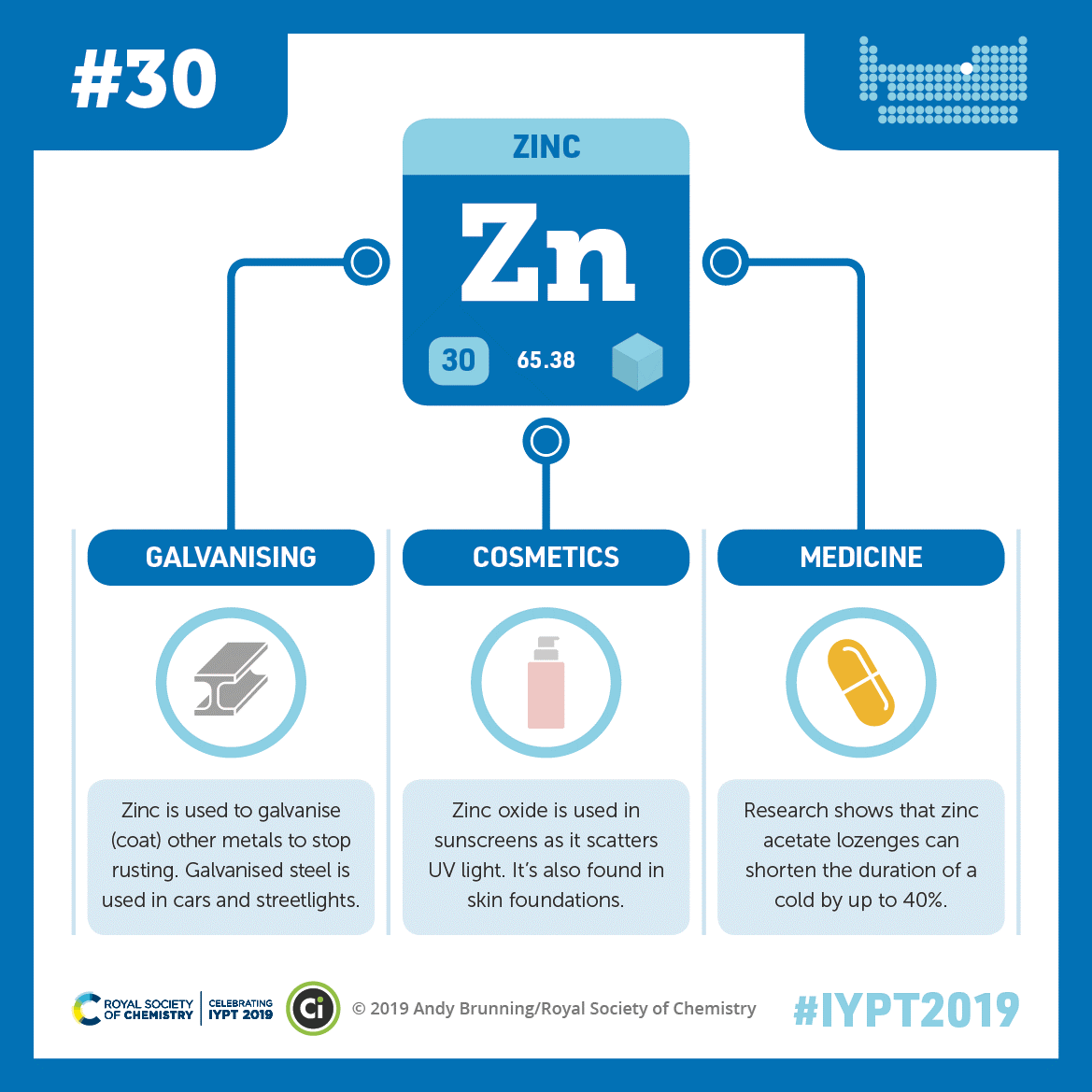 Zinc may help shorten colds, and it’s part of a compound that can protect skin from ultraviolet light. The element is also used to coat other metals and prevent rusting. Credit: Compound Interest. CC BY-NC-ND 4.0. Click to enlarge
Zinc may help shorten colds, and it’s part of a compound that can protect skin from ultraviolet light. The element is also used to coat other metals and prevent rusting. Credit: Compound Interest. CC BY-NC-ND 4.0. Click to enlarge


 ACTIV clinical trials will evaluate the safety and efficacy of COVID-19 treatments and vaccines. Credit: iStock.
ACTIV clinical trials will evaluate the safety and efficacy of COVID-19 treatments and vaccines. Credit: iStock.
 Credit: Liyang Xiong and Lev Tsimring, BioCircuits Institute, UCSD.
Credit: Liyang Xiong and Lev Tsimring, BioCircuits Institute, UCSD.
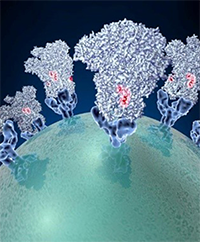 Spike proteins on the surface of a coronavirus. Credit: David Veesler, University of Washington.
Spike proteins on the surface of a coronavirus. Credit: David Veesler, University of Washington.
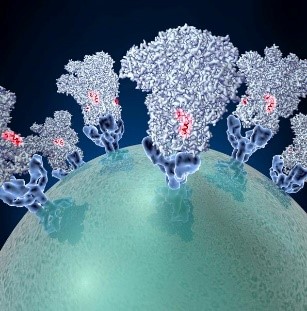 Spike proteins on the surface of a coronavirus. Credit: David Veesler, University of Washington.
Spike proteins on the surface of a coronavirus. Credit: David Veesler, University of Washington.
 A fruit fly expressing GFP. Credit: Jay Hirsh, University of Virginia.
A fruit fly expressing GFP. Credit: Jay Hirsh, University of Virginia.
 Dr. Franco-Ortiz (second from right) with students during a Coaching for Resiliency workshop session. Credit: Ivonne Bayron-Huertas, Ph.D.
Dr. Franco-Ortiz (second from right) with students during a Coaching for Resiliency workshop session. Credit: Ivonne Bayron-Huertas, Ph.D.