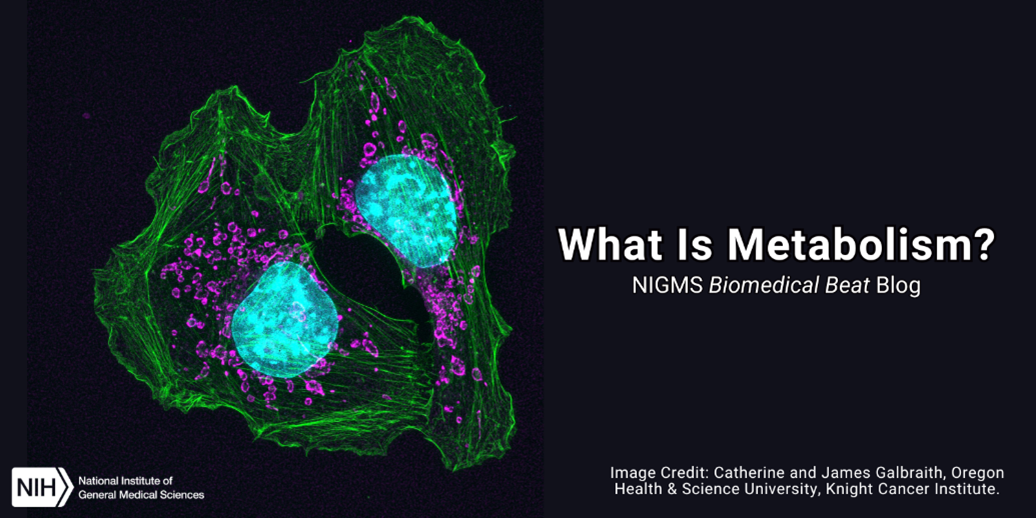
You’ve likely heard someone attribute their body size to a fast or slow metabolism. But did you know there’s much more to metabolism than calories burned? Metabolism includes all the chemical changes that occur as our bodies use enzymes to break down food, medicines, and biological substances as well as produce energy and materials needed for growth.
The Two Sides of Metabolism
Our bodies have many metabolic pathways, but they all fall into two main categories: catabolic and anabolic. Catabolic pathways break down complex molecules into simpler ones, usually releasing energy in the process. For example, catabolic pathways turn large carbohydrate molecules from our food into simple sugars, such as glucose. Some of the most well-known catabolic pathways then convert the simple sugar glucose into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a molecule that cells commonly use as an energy source.
Continue reading “What Is Metabolism?”