Did you know that molecules can be unionized? But it doesn’t mean they form a labor union. In chemistry, unionized (pronounced “un-ionized”) is the opposite of ionized, which means “electrically charged.”



Biomedical Beat Blog – National Institute of General Medical Sciences
Follow the process of discovery
Did you know that molecules can be unionized? But it doesn’t mean they form a labor union. In chemistry, unionized (pronounced “un-ionized”) is the opposite of ionized, which means “electrically charged.”

Did you know that kids aren’t the only ones playing around in sandboxes? The term sandbox may evoke a childhood memory of sensory play, but it’s also used to describe a virtual environment where someone can learn from digital products.

The word organic is often used to talk about fruits and vegetables that have been produced in a specific way, typically without the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. But to chemists, organic refers to carbon-containing compounds that are the basis for all living organisms. Ironically, the chemicals prohibited in the farming of organic produce are usually organic molecules.

Organic chemists study, create, and explore carbon-containing molecules. Most organic molecules contain carbon and hydrogen, but they can also include other elements like nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and more. Organic compounds are all around you, from the phospholipids in your body that make up your cell membranes and the NSAID pain reliever that might be in your medicine cabinet to the fabric of the shirt you’re wearing.
Continue reading “In Other Words: What’s It Mean to Be Organic?”The word media may make many of us think about media outlets where we get our news or social media where we keep up with friends. But to biomedical researchers, media is a nutrient-rich liquid that fuels cell cultures—groups of cells grown in a lab. Scientists grow many types of cultures in media, from bacteria to human cells. They use these cultures to learn about basic biological processes and to develop and test new medicines.

You might first think about sports when you hear the word base, but not all bases are on the baseball diamond. In chemistry, a base is a molecule that reacts with an acid, often by accepting a proton from the acid or from water. Baking soda and dish soap are common bases.

When we encounter the word mole, some of us might think of a small, fuzzy animal that burrows in gardens, or perhaps the common, pigmented marks on our skin. But in chemistry, the mole is a key unit of measurement; its name is derived from the word molecule. Similar to how “dozen” is another way of saying 12, “mole” is another way of saying 602,214,076,000,000,000,000,000 (that’s about 602 billion trillion), specifically for elementary entities such as molecules and atoms. Scientists sometimes abbreviate this number as 6.02 x 1023, which is why Mole Day is celebrated from 6:02 a.m. to 6:02 p.m. on October 23 each year.

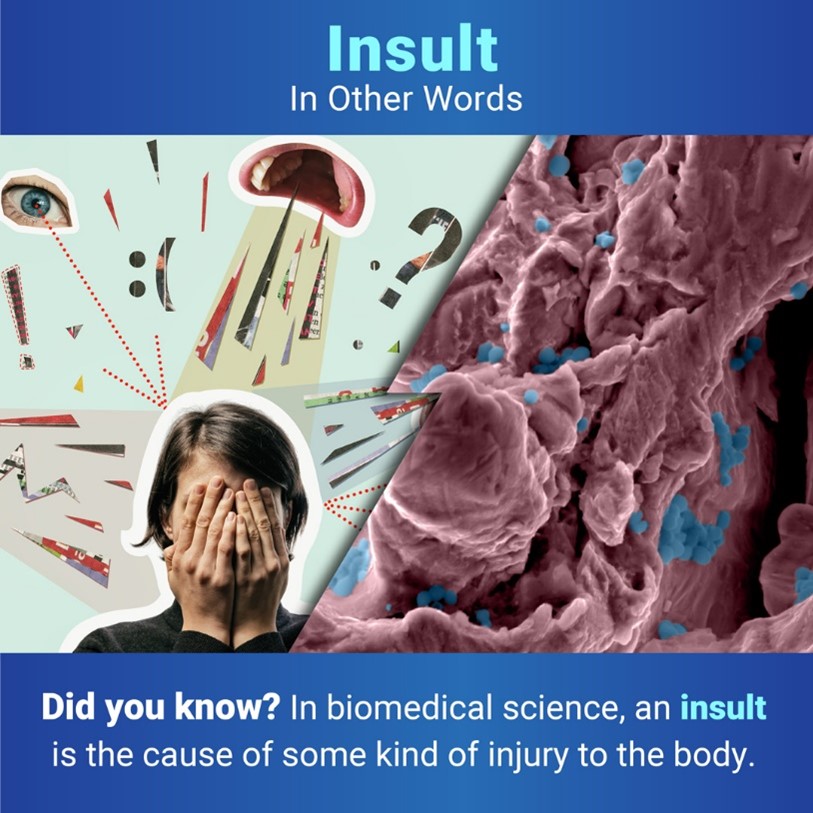
You probably think of a rude or offensive remark when you think of the word insult, but to biomedical researchers, an insult is the cause of some kind of injury to the body. Insults can come in a variety of forms, such as an infection or a physical trauma.
The word culture may make you think of a flag, style of clothing, celebration, or some other tradition associated with a particular group of people. But in biomedical science, a culture is a group of cells grown in a lab. Scientists use cultures to learn about basic biological processes and to develop and test new medicines.

The Birth of a Culture
Scientists can grow many types of cells as cultures, from bacteria to human cells. To create a culture, a researcher adds cells to a container such as a Petri dish along with a mix of nutrients the cells need to grow and divide. The exact recipe varies depending on the cell type. (Because many lab containers were historically made of glass, researchers sometimes refer to studies that use cultures as in vitro—Latin for “in glass.”) Once the cells multiply and fill their container, researchers split the culture into new containers to produce more.
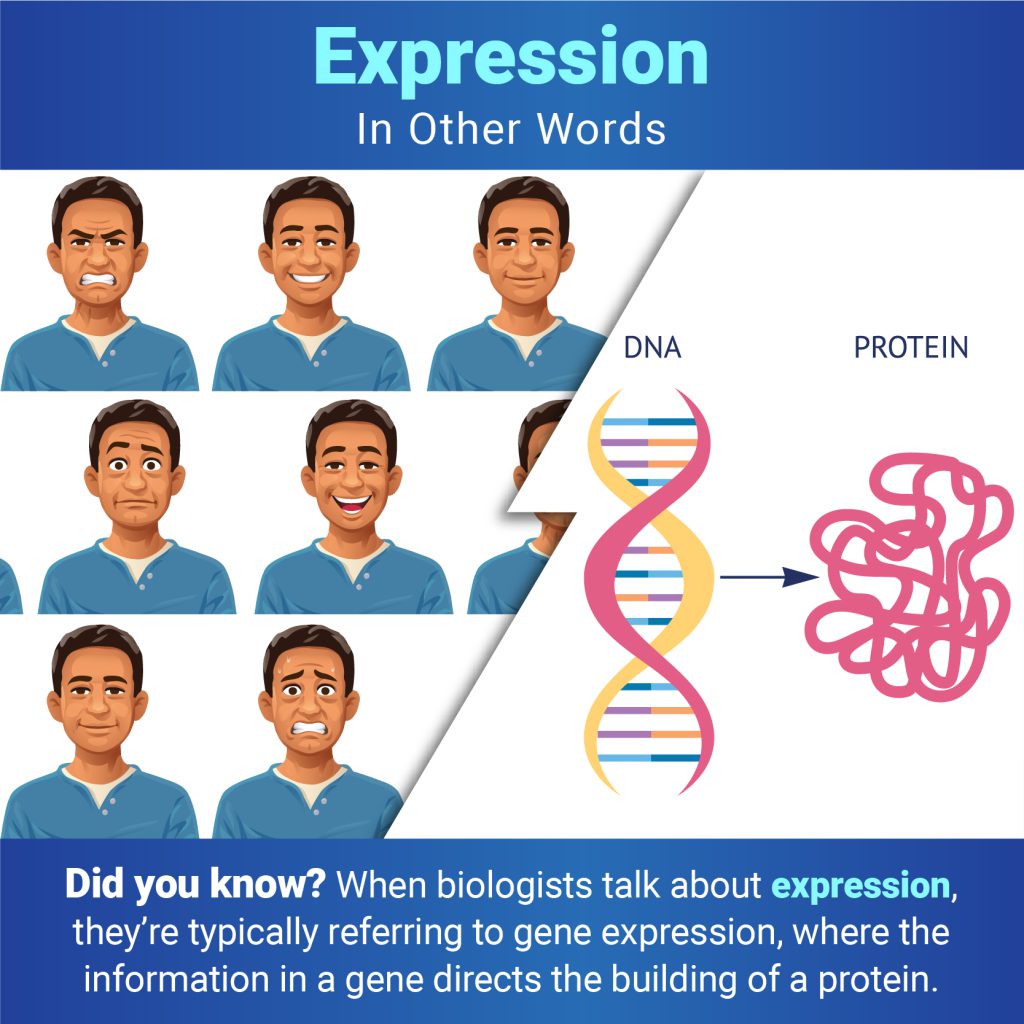
Continue reading “In Other Words: Not All Cultures Are Human”When you encounter the word expression, you may think of a smile, a grimace, or another look on someone’s face. But when biologists talk about expression, they typically mean the process of gene expression—when the information in a gene directs protein synthesis. Proteins are essential for virtually every process in the human body.
Many of us learned in English class that an antagonist is a person or thing that a hero fights. But in biomedical science, an antagonist is a molecule that binds to a cellular receptor to prevent a response, such as a muscle contraction or hormone release. Antagonists can be important medical treatments, like the antagonist naloxone—also known as Narcan —that can reverse an opioid overdose.
