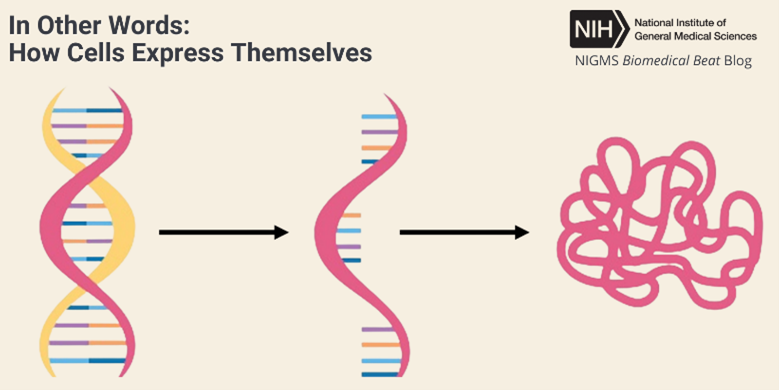
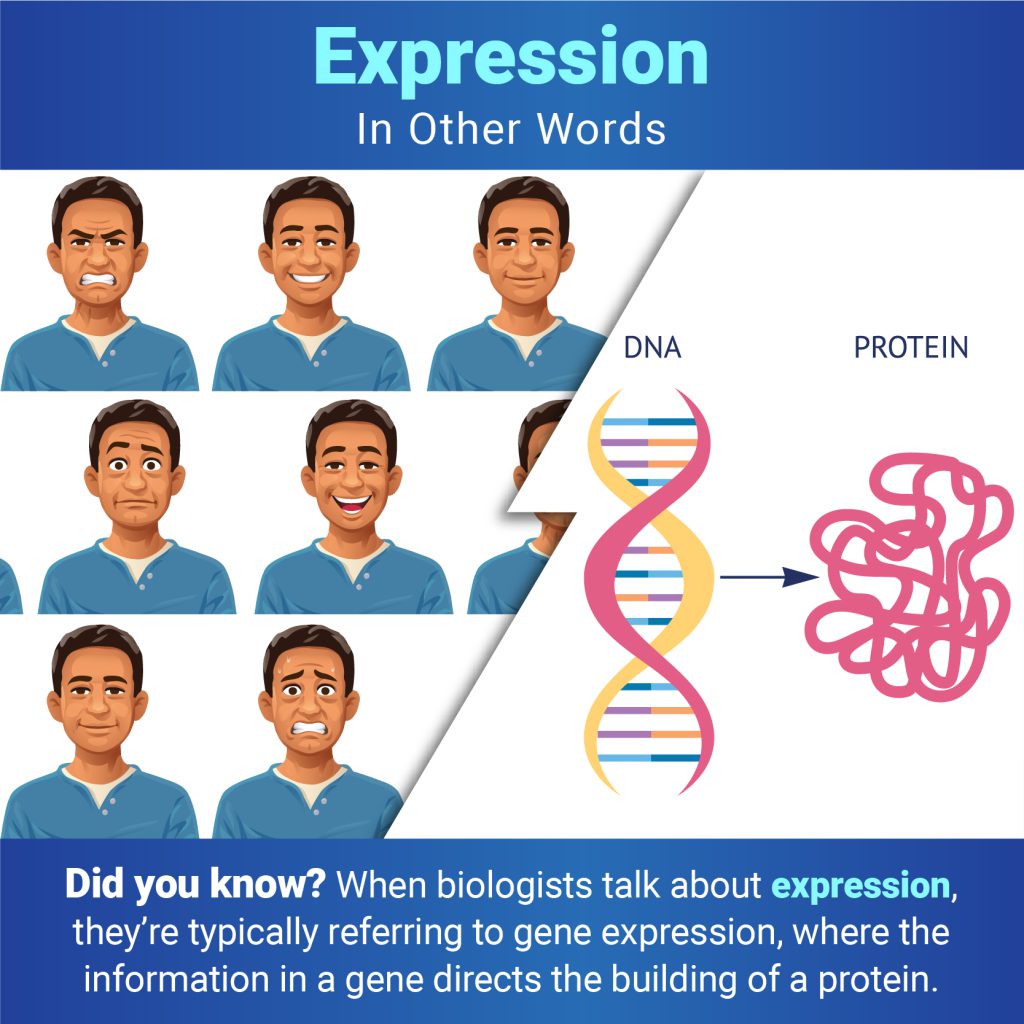
Some might think that protein is only important for weightlifters. In truth, all life relies on the activity of protein molecules. A single human cell contains thousands of different proteins with diverse roles, including:
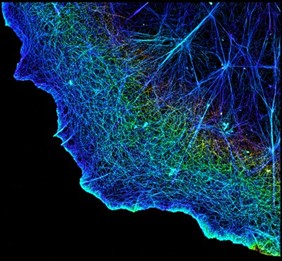
- Providing structure. Proteins such as actin make up the three-dimensional cytoskeleton that gives cells structure and determines their shapes.
- Aiding chemical reactions. Many proteins are biological catalysts called enzymes that speed up the rate of chemical reactions by reducing the amount of energy needed for the reactions to proceed. For example, lactase is an enzyme that breaks down lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Those with lactose intolerance don’t produce enough lactase to digest dairy.
- Supporting communication. Some proteins act as chemical messengers between cells. For example, cytokines are the protein messengers of the immune system and can increase or decrease the intensity of an immune response.









 Protein Data Bank’s 50 years logo. Credit: PDB website.
Protein Data Bank’s 50 years logo. Credit: PDB website.


