“One thing that we try to develop in students is a sense of belonging and scientific identity,” says Edwin Barea-Rodriguez, Ph.D., the director of the Research Training Initiative for Student Enhancement (RISE) program at the University of Texas, San Antonio (UTSA). The program provides undergraduate and graduate students from underrepresented backgrounds with research experiences, professional development opportunities, and faculty mentorships. The UTSA RISE program has helped hundreds of students build strong foundations for scientific careers over its more than 20-year history. Here, we share the stories of three students who have benefited from RISE.
Support Beyond the Lab

After earning her bachelor’s degree in biochemistry, Kaira Church knew she loved research but wasn’t sure if graduate school was right for her. She took a job as a lab technician in the research group of Astrid Cardona, Ph.D., a professor of molecular microbiology and immunology at UTSA, where she learned firsthand what being a graduate student entailed. She was also introduced to RISE and was impressed by the variety of opportunities it offered. She decided to pursue a Ph.D. and applied to the program.
Kaira is now in her fourth year as a RISE trainee. “I really like the professional development and the networking that RISE offers,” she says. “A lot of science majors are stuck in the lab all the time. RISE ensures that we’re meeting people in our field so we have plenty of job opportunities when we graduate.”
Continue reading “Biomedical Researchers RISE From the University of Texas, San Antonio”
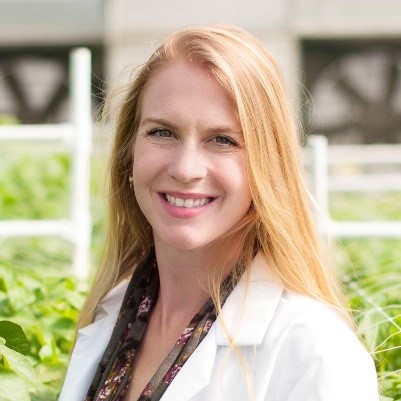




 Dr. Darden with her mentor, Dr. Philip Efron. Credit: Courtesy of Lyle Moldawer, Ph.D.
Dr. Darden with her mentor, Dr. Philip Efron. Credit: Courtesy of Lyle Moldawer, Ph.D.
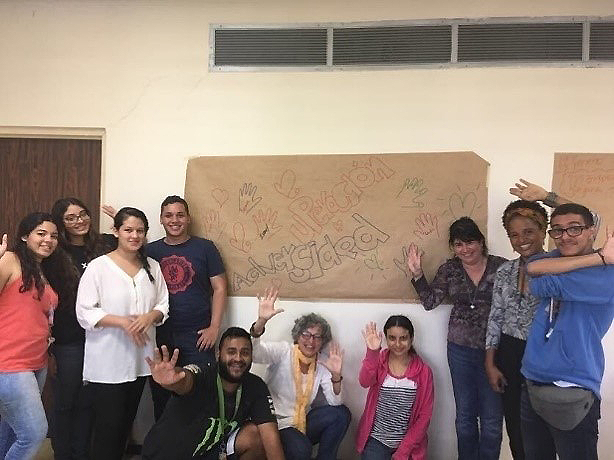

 Dr. Franco-Ortiz (second from right) with students during a Coaching for Resiliency workshop session. Credit: Ivonne Bayron-Huertas, Ph.D.
Dr. Franco-Ortiz (second from right) with students during a Coaching for Resiliency workshop session. Credit: Ivonne Bayron-Huertas, Ph.D.