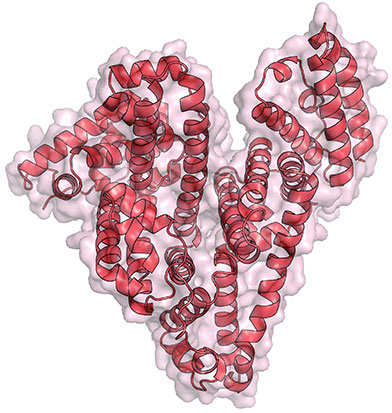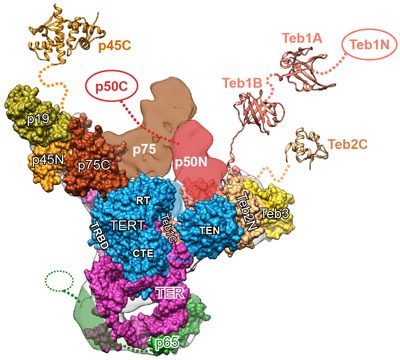
The image here is the “front view” of telomerase, with the enzyme’s components shown in greater detail than ever before. Credit: UCLA Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry.
Like the features of a cat in a dark alley, those of an important enzyme called telomerase have been elusive. Using a combination of imaging techniques, a research team led by Juli Feigon  of the University of California, Los Angeles, has now captured the clearest view ever of the enzyme.
of the University of California, Los Angeles, has now captured the clearest view ever of the enzyme.
Telomerase maintains the DNA at the ends of our chromosomes, known as telomeres, which act like the plastic tips on the ends of shoelaces. In the absence of telomerase activity, telomeres get shorter each time our cells divide. Eventually, the telomeres become so short that the cells stop dividing or die. On the other hand, cells with abnormally high levels of telomerase activity can constantly rebuild their protective chromosomal caps. Telomerase is particularly active within cancer cells. Continue reading “Seeing Telomerase’s ‘Whiskers’ and ‘Toes’”