This time of year, many creepy crawlies take center stage to frighten people of all ages. To celebrate Halloween, we’ve conjured up a slideshow of fascinating but spooky species that NIGMS-funded scientists study. Some of these creatures drink blood like vampires, while others—frogs, worms, flies, and salamanders—are perfect cauldron ingredients for a witch’s brew. Check out the slideshow—if you dare!
Continue reading “Slideshow: Creepy Crawlies”Tag: Cool Images
Cool Images: Radiant in Red
Happy Valentine’s Day! In place of red roses, we hope you’ll accept a bouquet of beautiful scientific images featuring rich, red hues. Be sure to click all the way through to see the festive protein flowing through your blood!
For more scientific photos, illustrations, and videos in all the colors of the rainbow, visit our image and video gallery.
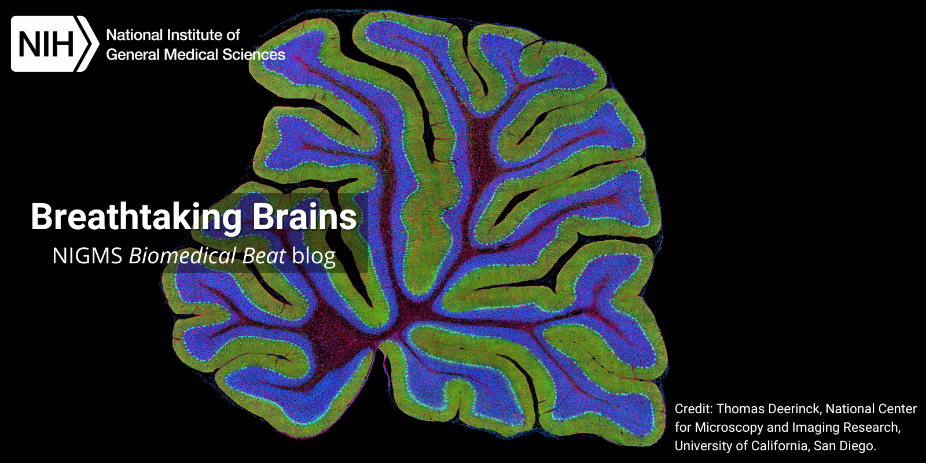
Continue reading “Cool Images: Radiant in Red”Slideshow: Breathtaking Brains
The average human brain is only about 3 pounds, but this complex organ punches well above its weight, acting as the control center for the whole body. Many of the brain’s intricacies still aren’t fully understood. To gain more insight into brain processes, scientists often peer into the brains of research organisms such as fruit flies and mice. These organisms have shed light on how our brains maintain circadian rhythms, how neuropsychiatric disorders develop, and more.
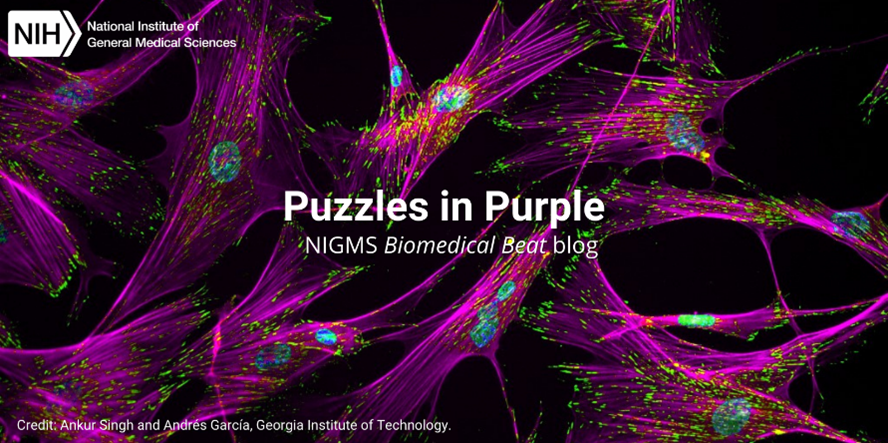
Continue reading “Slideshow: Breathtaking Brains”Photo Quiz: Puzzles in Purple
To make naturally colorless biological structures easier to study, scientists often use fluorescent tags and other tools to color them. Here, we feature images with purple hues and pair them with questions to test your knowledge of basic science concepts.
Visit our image and video gallery for more scientific photos, illustrations, and videos in all the colors of the rainbow.
Continue reading “Photo Quiz: Puzzles in Purple”Slideshow: Circles of Life
Every year on March 14, many people eat pie in honor of Pi Day. Mathematically speaking, pi (π) is the ratio of a circle’s circumference (the distance around the outside) to its diameter (the length from one side of the circle to the other, straight through the center). That means if you divide the circumference of any circle by its diameter, the solution will always be pi, which is roughly 3.14—hence March 14, or 3/14. But pi is an irrational number, which means that the numbers after the decimal point never end. With the help of computers, mathematicians have determined trillions of digits of pi.
To celebrate Pi Day, check out this slideshow of circular microbes, research organisms, and laboratory tools (while you enjoy your pie, of course!). To explore more scientific photos, videos, and illustrations, visit our image and video gallery.
Continue reading “Slideshow: Circles of Life”Five Outstanding Stories From 2022
Throughout 2022, we shared the stories of dozens of NIGMS-supported researchers, trainees, and programs. We also highlighted new STEM education resources, tested your knowledge with quizzes, showcased extraordinary scientific images, and more. To celebrate the upcoming new year, we’re highlighting five of our most popular posts from 2022. Check out the list below, and let us know in the comments section which of this year’s posts you liked best!
Continue reading “Five Outstanding Stories From 2022”Slideshow: Mitosis Masterpieces
The intricate process of mitosis—a cell splitting into two identical daughter cells—plays a pivotal role in sustaining life. Many scientists study this process to understand what’s needed for it to progress normally and why it sometimes goes awry, such as in cancer. During their research, the scientists often create eye-catching images and videos, and we showcase some of those visuals here.
Continue reading “Slideshow: Mitosis Masterpieces”Cool Images: Spooky and Spectacular
It’s the spookiest time of the year! To celebrate Halloween, we’re showcasing scientific images that capture the spirit of the holiday, from a brain shaped like a bat to protein “cobwebs” in a quail embryo. Check out our image and video gallery for even more scientific photos, illustrations, and videos.
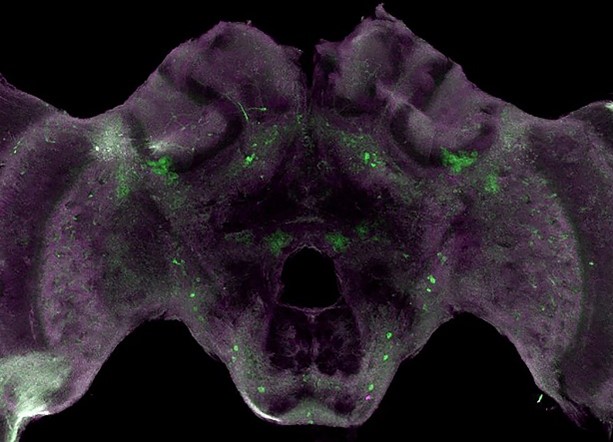

This image may bring to mind a bat spreading its wings, or you may feel like a skull is peering at you, but what’s actually shown is a honeybee brain. The bright-green spots are tyrosine hydroxylase, an enzyme that allows the brain to produce dopamine. Dopamine is involved in many important functions—such as the ability to experience pleasure—in both bees and humans.
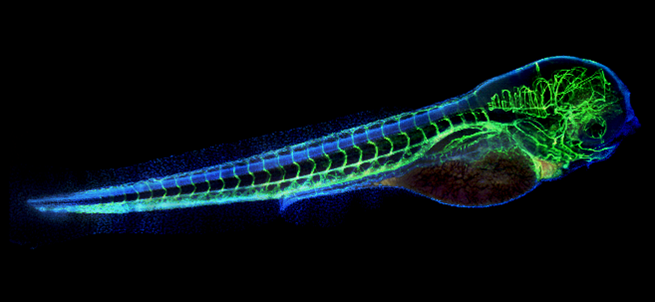
The eerie green “skeleton” in this photo is really the vasculature (blood vessels) of a zebrafish embryo. The blue areas are cell bodies. Zebrafish are useful research organisms for studying development because their eggs and embryos are see-through, making it easy for scientists to watch changes take place.
Researchers edited the genes of these creepy-crawly mosquito larvae using a technique called CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats). This species of mosquito, Culex quinquefasciatus, can transmit diseases including West Nile virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, and avian malaria. The gene-editing toolkit used on these larvae could ultimately help stop Culex quinquefasciatus from spreading pathogens.
The “cobwebs” in this image are actually a protein called vimentin in a quail embryo. The green spots are cell nuclei. Vimentin is part of the cytoskeleton and helps cells maintain their structure and resist mechanical stress. The protein is found in many animals and in humans.
Cool Images: Beautiful Bits of Blue
Most cells are naturally colorless, which is why scientists often use fluorescent tags and other tools to color cell structures and make them easier to study. (Check out the Pathways imaging issue for more on scientific imaging techniques). Here, we’re showcasing cell images that feature shades of blue. Visit our Image and Video Gallery for additional images of cells in all the colors of the rainbow, as well as other scientific photos, illustrations, and videos.
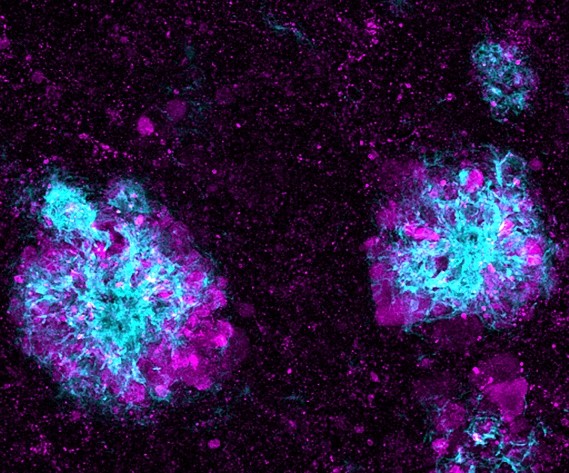
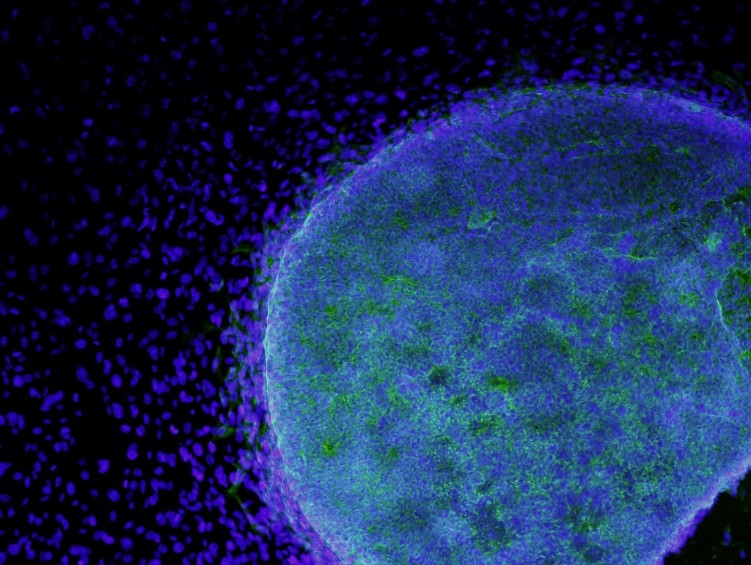
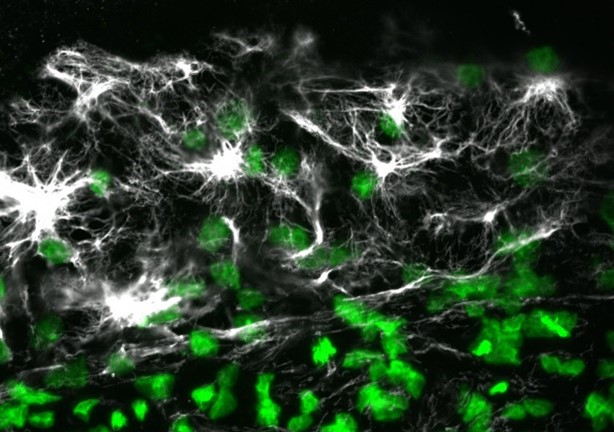
This image shows lysosomes (purple) within nerve cells that surround amyloid plaques (blue) in a research model of Alzheimer’s disease. Lysosomes help the body dispose of proteins and other molecules that have become damaged or worn out. Scientists have linked the accumulation of lysosomes around amyloid plaques to impaired waste disposal in nerve cells. This impairment ultimately causes nerve cell death, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease.
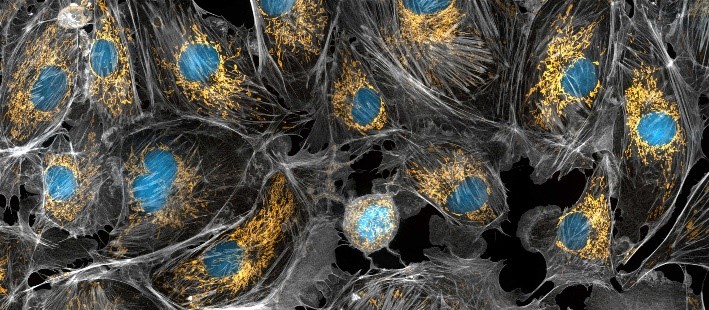
Mitochondria appear in yellow and cell nuclei in blue in this photo of cow cells. The gray webs are the cells’ cytoskeletons. Mitochondria generate energy, nuclei store DNA, and the cytoskeleton gives cells shape and support.
Here, stem cells (light blue) are growing on fibroblasts (dark blue). Stem cells are of great interest to researchers because they can develop into many different cell types. Fibroblasts are the most common cell type in connective tissue. They secrete collagen proteins that help build structural frameworks, and they play an important role in wound healing.
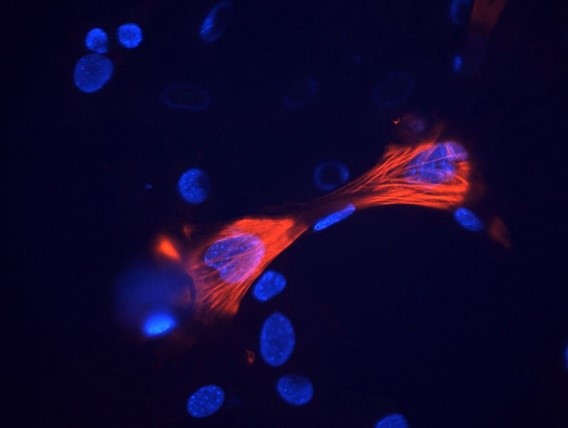
These smooth muscle cells were grown from stem cells. Smooth muscle cells are found in the walls of certain organs, such as the stomach, and can’t be controlled voluntarily. Red indicates smooth muscle proteins, and blue indicates nuclei.
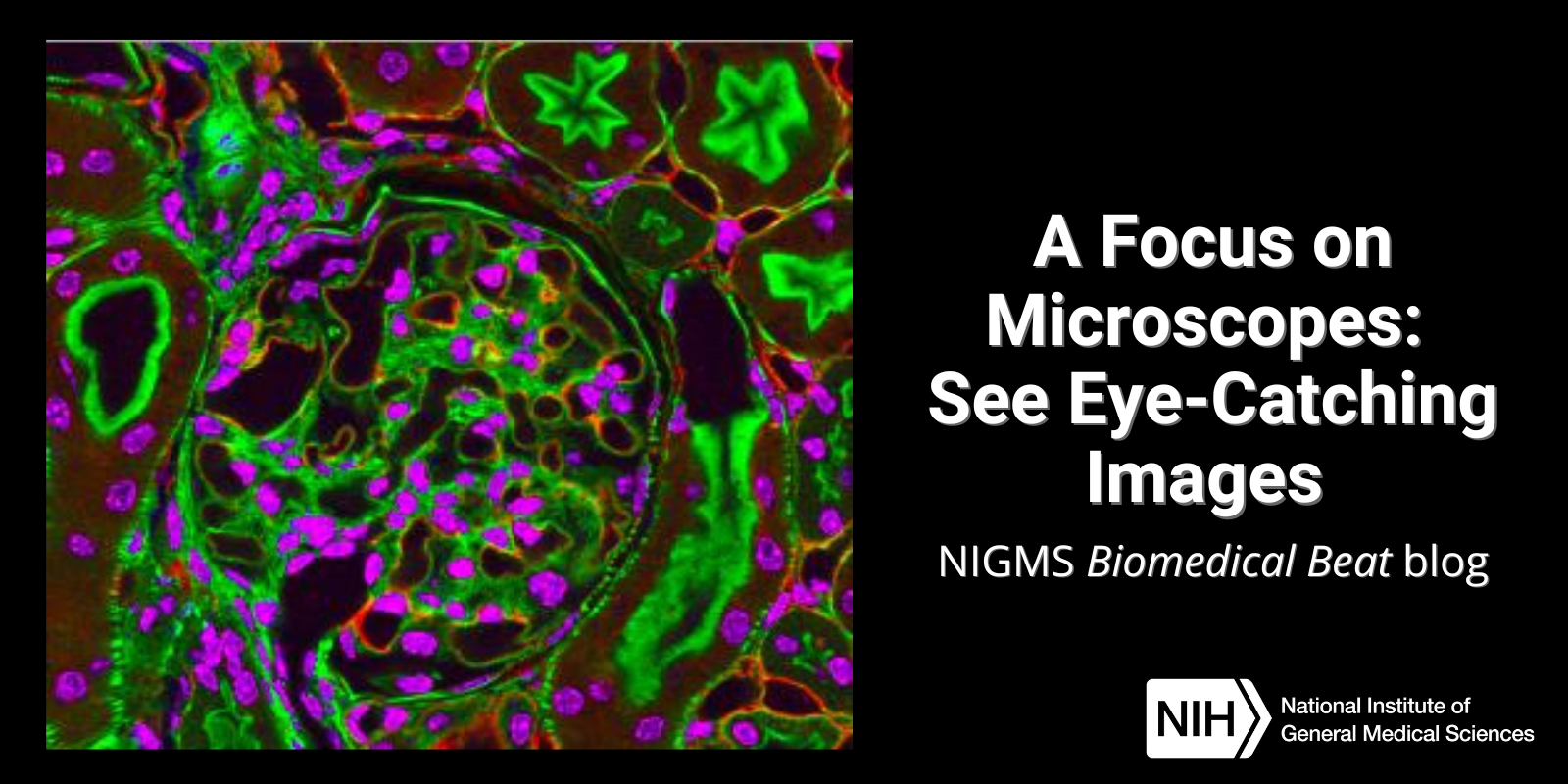
A Focus on Microscopes: See Eye-Catching Images
Have you ever wondered what creates striking images of cells and other tiny structures? Most often, the answer is microscopes. Many of us have encountered basic light microscopes in science classes, but those are just one of many types that scientists use. Check out the slideshow to see images researchers have captured using different kinds of microscopes. For even more images of the microscopic world, visit the NIGMS Image and Video Gallery.
Continue reading “A Focus on Microscopes: See Eye-Catching Images”