Educator’s
Corner

Welcome to the Biomedical Beat Educator’s Corner! This free resource is designed for educators to build on the existing NIH STEM content, like topics from our Pathways collaboration with Scholastic and other basic science areas, through the integration of supplemental material in Biomedical Beat blog posts. The Educator’s Corner is intended to give you additional tools to use in your lesson plans.
Below you’ll find a carefully curated list of blog posts from NIGMS that connect topically to STEM categories. We also provide suggestions for how to use the posts as educational supplements.









Genetics
What Is Genetics?
ABOUT THE POST
The first post in our miniseries on genetics introduces the study of genes and how they're passed from parents to children. Genes are segments of DNA—the blueprints for our bodies—that provide instructions for making important molecules. The vast majority of DNA is the same among all people, but small differences affect appearance and health.
ACTIVITY
How Are Physical Features and Health Conditions Inherited?
ABOUT THE POST
Family members often share some traits but not others. The combination of similarities and differences largely results from how people inherit and express genes. This post discusses how DNA passes from parents to children and how the instructions in genes lead to observable traits, such as physical features and health conditions.
ACTIVITY
How Do Scientists Study Genes?
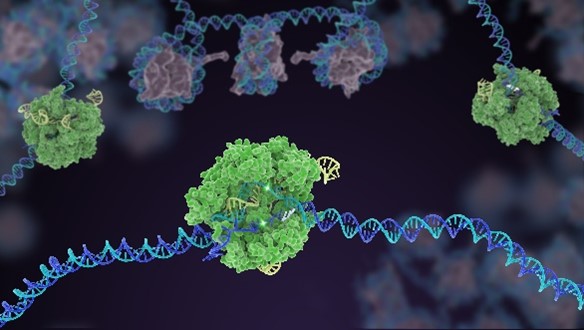
ABOUT THE POST
Researchers learn about human genes through a variety of tools and techniques, such as DNA sequencing and genome editing. In addition to investigating human DNA, scientists use these tools and techniques to study the DNA of other organisms. Thanks to similarities across the genomes of living things, this research has helped us to better understand human health and disease and to learn about unique traits of other organisms.
ACTIVITY
Quiz: Gauge Your Genetics Knowledge

ABOUT THE POST
Our genetics miniseries covers the basics of the field—from how people inherit genes to how researchers study them. This quiz, the final post in the series, tests how much students have learned. Can they answer all six questions correctly?
ACTIVITY
Basic Science Concepts
How Do Cells Recycle and Take Out the Trash?
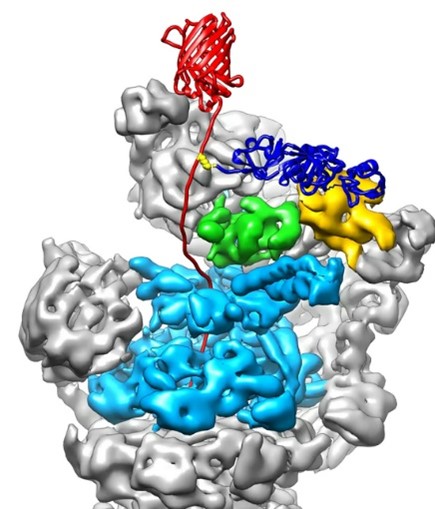
ABOUT THE POST
You know the phrase “reduce, reuse, recycle” to save the planet? Our cells take that to heart to care for our bodies: Their efficiency reduces waste, their enzymes are reusable, and they recycle as much of their garbage as possible. But while our cells are excellent stewards of our bodies, sometimes they do have trash. They have systems in place to ensure they get the most out of their trash, but sometimes these systems go awry and cause diseases like Alzheimer's.
ACTIVITY
What Is CRISPR?
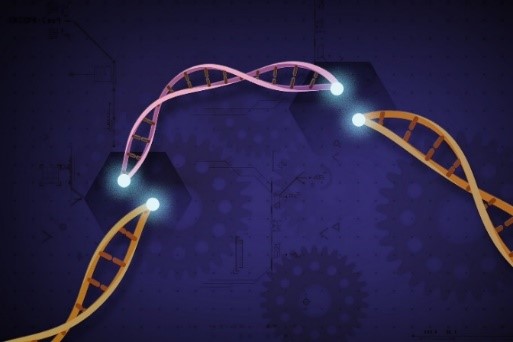
ABOUT THE POST
In the 1980s, researchers discovered odd, repeating sequences in the genomes of certain bacterial species, later named CRISPR sequences. Now, scientists use the CRISPR-Cas9 system in the laboratory as a gene-editing tool to improve our understanding of human biology, and medical doctors can use it to treat some diseases, like sickle cell disease.
ACTIVITY
How Many Ounces Are in a Cup—and Other Measurement Morsels

ABOUT THE POST
Do you find yourself frustrated when trying to convert between measuring units while baking? Find out how many ounces are in a cup and other measurement morsels—like what baking soda does to your chocolate chip cookies and why you (and scientists in the lab) need to be accurate in your measurements.
ACTIVITY
What Is a Neurotransmitter?
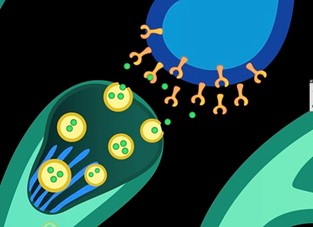
ABOUT THE POST
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that carry messages from one nerve cell to another and sometimes to muscles or glands. These chemicals help our bodies perform vital functions, such as breathing, sleeping, feeling pain and emotions, moving our limbs, and many others. This post describes how neurotransmitters work and how changes in their levels can contribute to, or help treat, disease.
ACTIVITY
Science Snippet: The Significance of Symbiotic Relationships

ABOUT THE POST
Symbiotic relationships are everywhere in nature and help species survive through interactions with one another. This post describes the different types of symbiosis and how symbiotic relationships can affect human health.
ACTIVITY
Quiz: Can You Solve These RNA Riddles?

ABOUT THE POST
RNA is an essential molecule for life. It helps translate the instructions of DNA into proteins. Researchers study RNA, looking for ways to use it to develop medicines, vaccines, and tests for certain diseases. This post tests RNA knowledge.
ACTIVITY
What Is Metabolism?
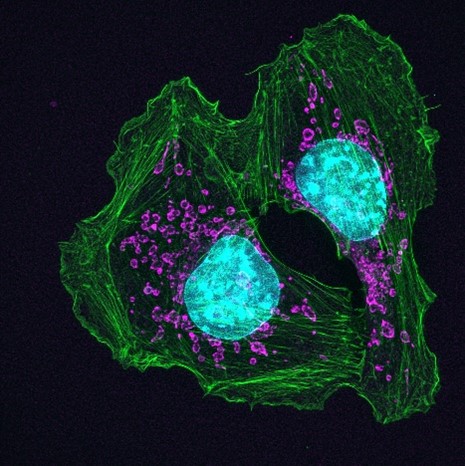
ABOUT THE POST
Metabolism encompasses all the chemical reactions our bodies use to build up and break down molecules to keep us alive and healthy. Our cells must constantly balance many metabolic pathways. If these pathways are disrupted, serious diseases can occur.
ACTIVITY
Science Snippet: Breaking Down Biodegradability

ABOUT THE POST
A common question in science is, “What can I do to keep our planet healthy?” Replacing traditional plastic with biodegradable plastic is one way to reduce the impact of plastic on the earth. Sometimes, plastic utensils or paper plates have a small logo indicating that they’re biodegradable. Materials that are biodegradable can be broken down into their building blocks by microorganisms such as bacteria, which extract the energy stored inside those small units.
ACTIVITY
What Is the Microbiome?
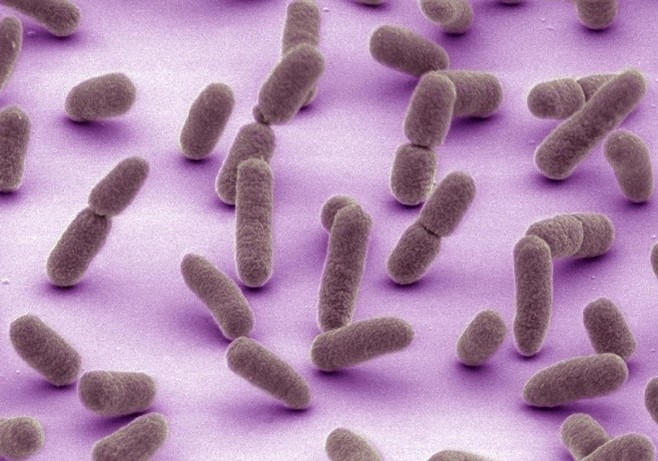
ABOUT THE POST
A microbiome is the collection of all the microbes—including bacteria, viruses, and fungi—that live in a certain environment. Much of the human microbiome is made up of friendly microbes that we rely on to keep us healthy. Disruptions to the microbial communities in our bodies can cause disease.
ACTIVITY
Immunology
What Is the Immune System?
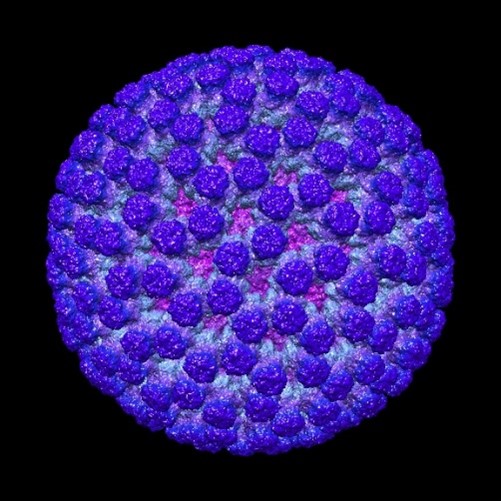
ABOUT THE POST
The first post in our miniseries on immunology introduces the immune system, which protects you from microbes that could cause infection. One important aspect of the immune system is its ability to remember the microbes it has seen before. This phenomenon, called immune memory, is a key part of vaccine science.
ACTIVITY
How Can the Immune System Go Awry?
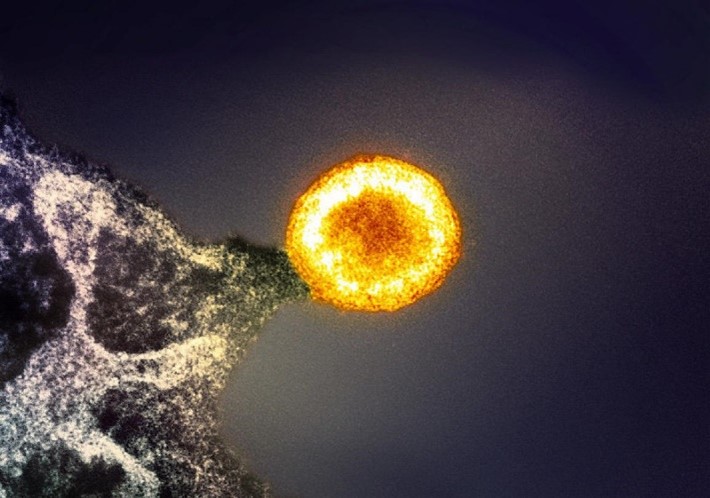
ABOUT THE POST
The second post in our immunology miniseries is all about diseases related to the immune system. The immune system’s job is to protect us from infectious intruders, but it sometimes gets confused and attacks the wrong cells, reacts to harmless substances, or fails to respond to intruders effectively.
ACTIVITY
What Does an Immunologist Do?
ABOUT THE POST
In our third post in the immunology miniseries, we talk about immunologists, who are researchers and doctors who study the immune system or treat patients with immune-related diseases. Learn more about the NIGMS grantees we’ve highlighted on Biomedical Beat who study the immune system.
ACTIVITY
Quiz: Do You Know Your Immune System?

ABOUT THE POST
Throughout our immunology miniseries, we introduce the many functions and components of the immune system and highlight NIGMS-supported researchers who study immunology. For the final post, test your knowledge with a quiz.
ACTIVITY
Pharmacology
What Is Pharmacology?

ABOUT THE POST
The first post in our pharmacology miniseries gives an overview of the research-based science situated at the intersection of chemistry, biology, and medicine. Pharmacologists explore how molecules and bodies interact, and their research can have major impacts to how we understand human health and how clinicians treat patients.
ACTIVITY
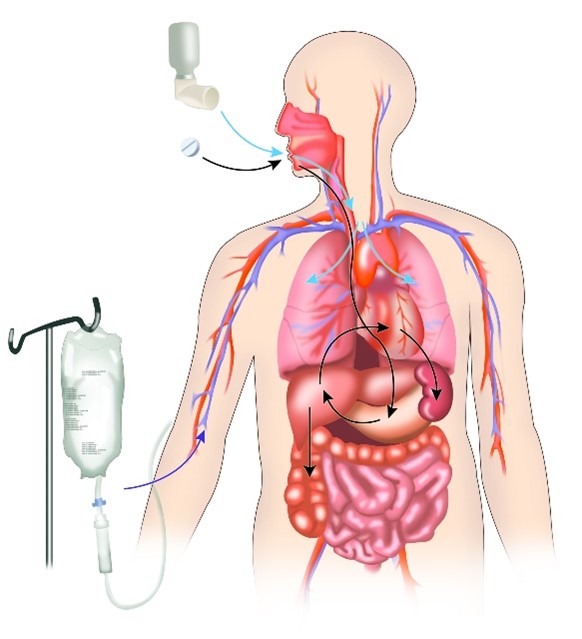
What Happens to Medicine in Your Body?
ABOUT THE POST
The second post in our pharmacology miniseries introduces pharmacokinetics, the study of how the body acts on a medicine. The post follows a medicine entering the body, finding its therapeutic target, and eventually leaving the body to answer the common question, “What happens to medicine in your body?”
ACTIVITY
How Do Medicines Work?

ABOUT THE POST
The third post in our pharmacology miniseries introduces pharmacodynamics, the study of how medicines act in the body. Most medicines bind to molecular targets, which results in their therapeutic effects. In this post, we explore how medicines act at different targets or directly upon the immune system and how pharmacologists help determine dosages that maximize a medicine’s effectiveness while minimizing side effects.
ACTIVITY
Quiz: Do You Know Pharmacology Facts?

ABOUT THE POST
The final post in our pharmacology miniseries discusses some areas of pharmacology that NIGMS-funded researchers study and puts your knowledge to the test with a quiz.
ACTIVITY
Becoming a Biomedical Scientist
How Can I Become a Biomedical Scientist?

ABOUT THE POST
Are any of your students particularly enamored with science? This post, the first in our new miniseries on becoming a scientist, lays out the different levels of education and training that scientists may have, from an undergrad degree to a Ph.D. and even postdoctoral work.
ACTIVITY
What Careers Can Biomedical Scientists Have?

ABOUT THE POST
There are many job options for students who love science and want to immerse themselves in it. This post highlights some of those options, such as being a biomedical science writer or a researcher at a university or private company.
ACTIVITY
Advice to Future Scientists

ABOUT THE POST
For the final post in our miniseries on becoming a scientist, we’re revisiting some advice NIGMS-funded researchers have for students who are interested in a science career path. Check out the full Q&As with these researchers if you missed them.
ACTIVITY
The Brain and Anesthesia Issue
All About Anesthesia
ABOUT THE POST
Anesthesia is a medical marvel that keeps patients from feeling pain. If you’ve ever had a surgery or even a minor procedure, you’ve probably benefited from it! In this post, we dive into the different types of anesthesia, its history, the way it works, and NIGMS-supported research on it.
ACTIVITY
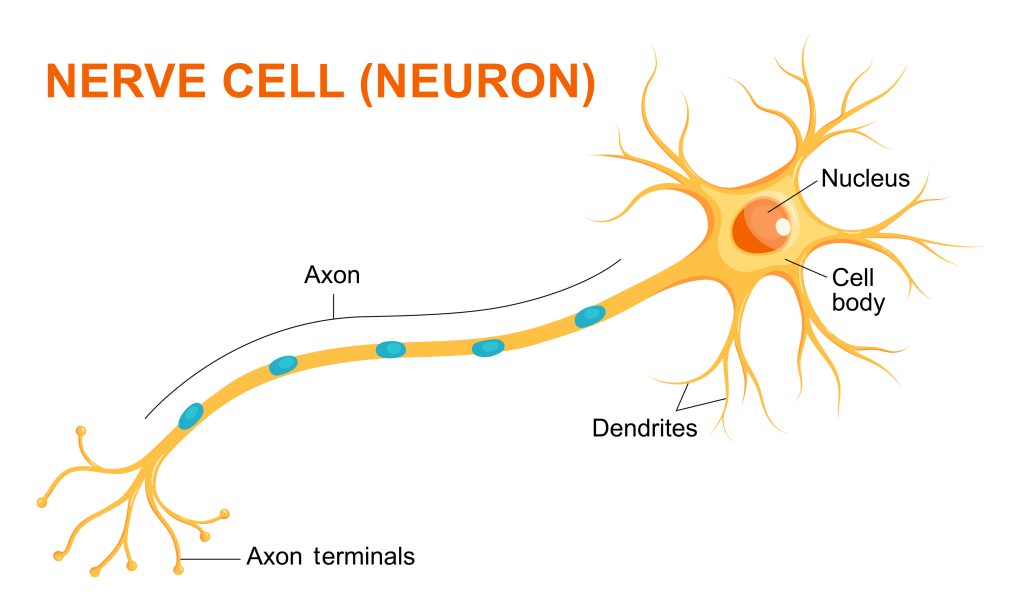
Science Snippet: Get to Know Your Nerve Cells
ABOUT THE POST
Did you know that some cells in our bodies use electricity to carry information? These nerve cells, or neurons, are fundamental for how we interact with our environment. In this post, we explore the role of nerve cells and describe NIGMS-supported research on them.
Nerve cells allow us to feel pain (among other things), and anesthetics, as described in Pathways, prevent us from feeling pain.
ACTIVITY
Biology Beyond the Lab: Using Computers to Study Life

ABOUT THE POST
Computers and mathematical methods are increasingly important tools for studying biology. In this post, we share the stories of a medical doctor who aims to use these tools to predict sepsis and a computer scientist who applies them to understand cell development pathways.
Pathways discusses machine learning as a possible way to discover a definitive biomarker for pain. This post explains how scientists use computers to study biological processes.
ACTIVITY
The Imaging Issue
Photo Quiz: Puzzles in Purple
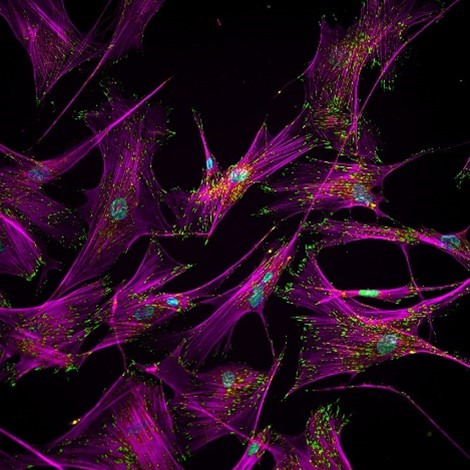
ABOUT THE POST
This quiz features eye-catching, purple-hued images paired with questions that test your knowledge of basic science concepts. The images were captured using some of the techniques described in Pathways.
ACTIVITY
Automating Cellular Image Analysis to Find Potential Medicines

ABOUT THE POST
Anne Carpenter, Ph.D., has developed software for analyzing images of cells that can identify signs of diseases and potential medicines to treat them. Thousands of researchers, including many at pharmaceutical companies, have adopted her computer program. Dr. Carpenter never imagined this achievement when she started her journey in science as a biologist without any computer science training.
Both this post and Pathways describes tools used for imaging microscopic biological structures such as cells.
ACTIVITY
Fifty Years of the Protein Data Bank!

ABOUT THE POST
Since 1971, the Protein Data Bank has served the scientific community as an open-access resource of 3D protein structures. To celebrate 50 years as a key resource in the community, we spotlight an educational board game that simulates the process of determining a protein’s structure. Knowing the structures of proteins and other biological molecules helps scientists understand their roles in human health and disease and leads to the discovery of new and more effective medications.
Researchers use many imaging techniques in determining protein (and other macromolecular) structures. Some of these techniques are described in Pathways, and others are introduced in this post.
ACTIVITY
Cool Video: A Biological Lava Lamp
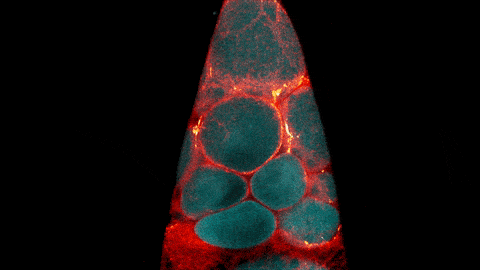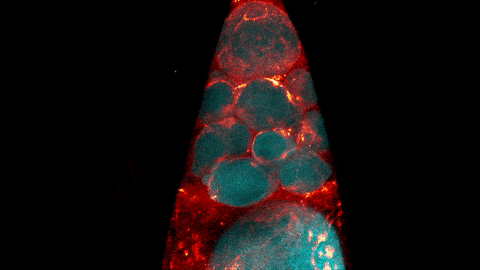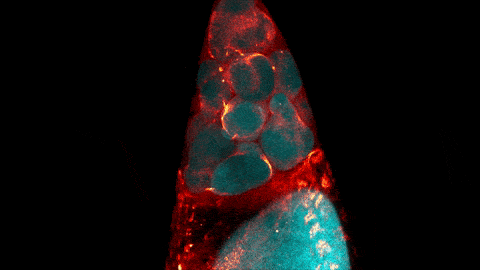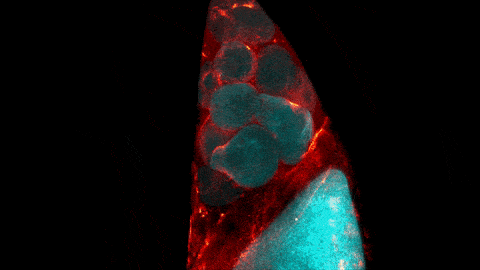
ABOUT THE POST
The glowing, twisting cells in this video look just like a bubbling lava lamp, but they actually show a step of egg cell development.
The video was taken using a confocal laser scanning microscopy (sometimes shortened to just “confocal microscopy”), one of the techniques mentioned in the Pathways timeline (1970s).
ACTIVITY
A Focus on Microscopes: See Eye-Catching Images
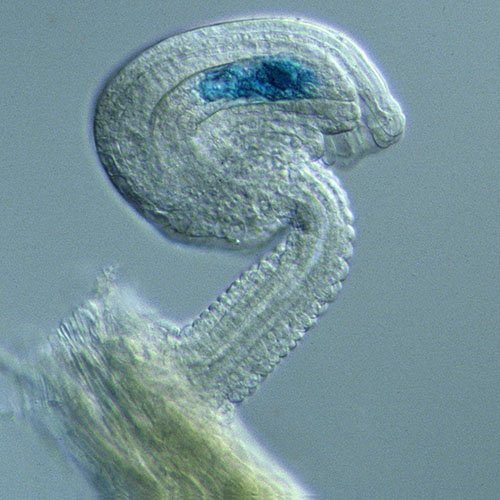
ABOUT THE POST
Did you know that there are many kinds of microscopes? Each offers its own advantages to researchers studying the tiny components of life, but all of them can capture eye-catching images.
The images in this post were taken using some of the imaging techniques described in Pathways.
DISCUSSION
Through the Looking Glass: Microscopic Structures in Many Sizes
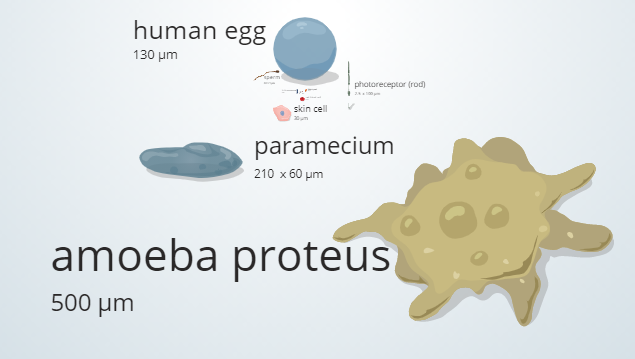
ABOUT THE POST
Microscopic structures can vary greatly in size. The largest objects that we view through microscopes are about 10 million times larger than the smallest!
The relative sizes in the microscopic world described in Pathways can be difficult to conceptualize. This post describes an interactive tool to view these relative sizes.
ACTIVITY
Superbugs
What Is Antibiotic Resistance?
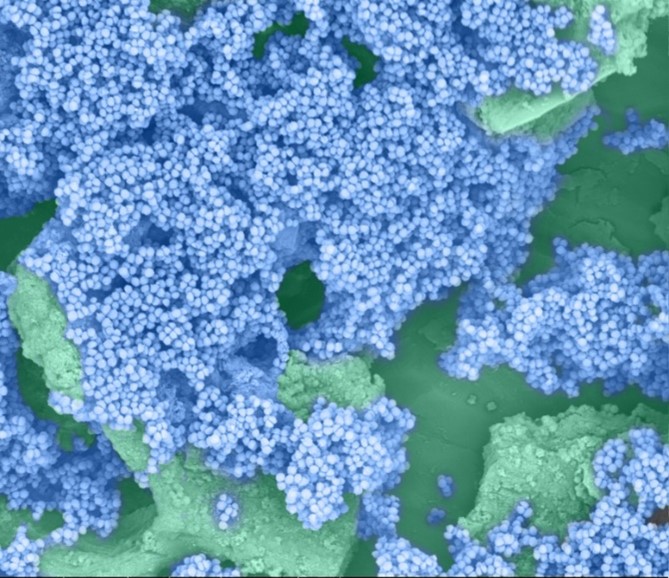
ABOUT THE POST
Antibiotic resistance is a growing problem where bacteria develop the ability to fend off the antibiotics we use to fight them. Infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria are difficult to treat and can be deadly. This post explains how bacteria become resistant to antibiotics and what you can do to help prevent that from happening—topics that Pathways also explores.
ACTIVITY
Antibiotic Resistance and Researchers Studying It

ABOUT THE POST
Test your knowledge of bacterial infections with this quiz, using examples from some of the scientists we’ve featured on the blog who explore new ways to fight antibiotic resistance. This post and Pathways discuss antibiotic resistance.
ACTIVITY
Science Snippet: Brush Up on Biofilms
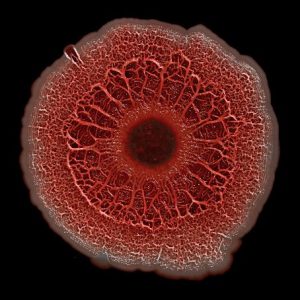
ABOUT THE POST
Microbes often form organized communities called biofilms. Some are useful to people, but others cause disease. Many NIGMS-supported researchers study biofilms and are developing ways to combat those that can threaten your health.
Pathways describes antibiotic-resistant superbugs, and this post describes biofilms, which are also antibiotic resistant.
DISCUSSION
Cool Images: Bewitching Bacteria
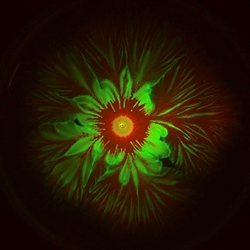
ABOUT THE POST
The effects of bacteria on our bodies range from helpful to life threatening. But regardless of their relationship to us, many species of bacteria can be surprisingly stunning.
This post shows pictures of bacteria, and Pathways is all about bacteria and superbugs.
ACTIVITY
Exploring Nature’s Treasure Trove of Helpful Compounds
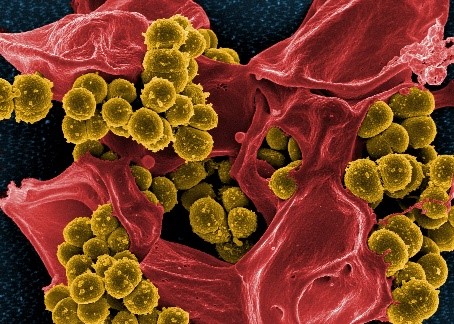
ABOUT THE POST
Compounds that plants, fungi, bacteria, and animals produce can sometimes help people as well. In fact, many medicines, molecules used in research, and other useful compounds originated in nature.
Natural products are a source for new antibiotics that may help us fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria and superbugs.
ACTIVITY
The Circadian Rhythms Issue
Why Am I So Tired?

ABOUT THE POST
Circadian rhythms are your internal timekeepers—they control daily activities such as when you go to sleep and wake up. When they fall out of sync with your environment, you may feel groggy and have trouble focusing.
ACTIVITY
Quiz: What Can Research Organisms Reveal About Health?

ABOUT THE POST
Research organisms such as fruit flies and mice help scientists better understand basic biological processes and develop treatments for human diseases. This interactive quiz tests your knowledge of these important creatures.
Much of what we know about circadian rhythms in humans was first discovered in research organisms.
ACTIVITY
Scientist Interview: Investigating Circadian Rhythms with Michael W. Young
ABOUT THE POST
When circadian rhythms are disrupted—for instance, by the beginning or ending of daylight saving time that occurs each March and November—we often feel “off” until our bodies adjust. But for some people, this adjustment never happens. Nobel laureate Michael W. Young, Ph.D., describes his current research on circadian rhythms and delayed sleep phase disorder in a short video interview.
The scientist interviewed in this post, Dr. Michael W. Young, was awarded the 2017 Nobel Prize for his research on circadian rhythms.
ACTIVITY
The Regeneration Issue
A Tale of Tails: How Reptile Regeneration Could Help Humans

ABOUT THE POST
Thomas Lozito, Ph.D., has been fascinated by lizards since he was about 4 years old. He now researches how they regrow their tails in hopes of unlocking secrets that could ultimately improve human healing. Within the next 10 years, Dr. Lozito aims to take his research a step closer to humans by enabling a mouse to regenerate its tail.
Both this post and Pathways feature Dr. Lozito and his research on regeneration.
ACTIVITY
Quiz Yourself to Grow What You Know About Regeneration

ABOUT THE POST
Do you know which tissues and organs the human body can regenerate? How about which animals can regrow entire limbs? Our quiz will test your knowledge of regeneration and regenerative medicine.
This post quizzes how much you know about regeneration, the topic of Pathways.
ACTIVITY
Interview With a Scientist: Unlocking the Secrets of Animal Regeneration With Alejandro Sánchez Alvarado

ABOUT THE POST
Alejandro Sánchez Alvarado, Ph.D., is making exciting discoveries in the field of regenerative medicine. For the last 2 decades, NIGMS has supported the work of his laboratory in studying flatworms to uncover the genetic and developmental basis of regeneration. In a short video interview, Sánchez Alvarado describes his research findings and how they might impact our health.
Both this post and Pathways feature Alejandro Sánchez Alvarado, Ph.D., and his work in regenerative medicine.
DISCUSSION
Basic Science Careers
How Research Works: Understanding the Process of Science

ABOUT THE POST
Have you ever wondered how scientific discoveries are made? Scientists follow the scientific method when they ask questions about the world around them. They perform experiments, analyze their results, and draw conclusions based on the results.
Pathways introduces the important role that scientists play in understanding the world around us, and all scientists use the scientific method as they make discoveries—which is explained in this post.
ACTIVITY
Any of Our Posts on Being a Scientist!

ABOUT THE POST
We regularly interview scientists to hear about their research and what led them to where they are in their careers. Check out our Q&As with:
- Evolutionary biologist William Ratcliff
- Biomolecular engineer Markita Landry
- Bioengineer César de la Fuente
- Organic chemist Elizabeth Parkinson
- Biochemist Alexis Komor
- Medicinal inorganic chemist Eszter Boros
- Immunoengineer Caroline Jones
- Clinician-scientist Faheem Guirgis
- And more in our Being a Scientist category
We also have posts highlighting some of the researchers featured in Pathways, including Computational biologist Melissa Wilson and Geneticist Michael Young.
Pathways discusses the importance of basic science, and these posts highlight researchers who study different fields of basic science.
DISCUSSION
Select a topic from the dropdown above to view blog posts that directly or indirectly connect to the STEM topics along with activity suggestions for how to use the posts as educational supplements.
Other Resources for Your Classroom
If you’re looking for other educational supplements, check out the short scientific posts in these series:
Find more educational content and curriculum supplements on our NIH-wide K-12 STEM resources website.
We’d love to hear how you’re using these resources or if there’s one you suggest that we add. Feel free to leave these comments below!





